Case : 来看两个共享counter变量的进程
Process 1
1 | while (true) { |
Process 2
1 | while (true) { |
在执行时
1 | counter++ |
相当于下面三行代码
1 | register1 = counter |
且
1 | counter-- |
相当于
1 | register2 = counter |
有可能下面的情况出现
(此处感谢
https://myfavs.win/2019/08/08/%E8%AE%B0%E5%BD%95-Hexo-%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%87%E7%9A%84%E5%9D%91/
解决了图片问题)
1.Critical Section
The important feature of the system is that, when one process is executing in its critical section, no other process is allowed to execute in its critical section. That is, no two processes are executing in their critical sections at the same time. The critical-section problem is to design a protocol that the processes can use to cooperate.
理解一下:一个进程在critical section里执行的时候,其他程序不可以进来。否则就会出现上述情况中的问题
Three Requirements
1.Mutual Exclusion
If process Pi is executing in its critical section, then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections.
基本就是字面意思
2. Progress
If no process is executing in its critical section and some processes wish to enter their critical sections, then only those processes that are not executing in their remainder sections can participate in deciding which will enter its critical section next, and this selection cannot be postponed indefinitely.
中文翻译: 如果没有进程在其临界区内执行且有进程需进入临界区,那么只有那么不在剩余区内执行的进程可参加选择,以确定谁能下一个进入临界区,且这种选择不能无限推迟;(wtf?????)
研究一番之后的理解:所有程序都在make progress而不是傻等。
- critical section里的程序,继续干自己的事
- critical section结束的还在remainder section的程序,继续把自己的干完,先别想着下次进来
- 其他程序,别傻等着,好好去想一想下一个谁进来
- 你们决定的过程要在有限时长内完成(无deadlock 或者 livelock 出现)
3.Bounded Waiting
There exists a bound, or limit, on the number of times that other processes are allowed to enter their critical sections after a entry section critical section exit section.
每个程序都会进入critical section 而不是starve forever.
2. Peterson Solution and Dekker’s Solution
Peterson
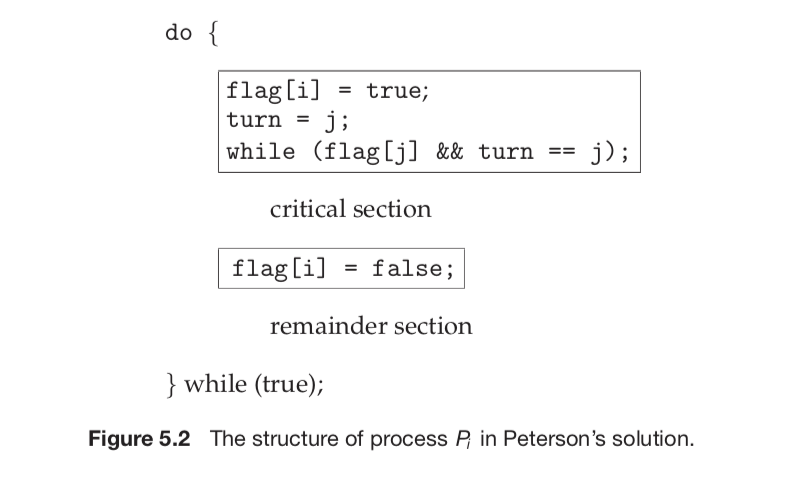
Dekker
There is a process on how versions change.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dekkers-algorithm-in-process-synchronization/